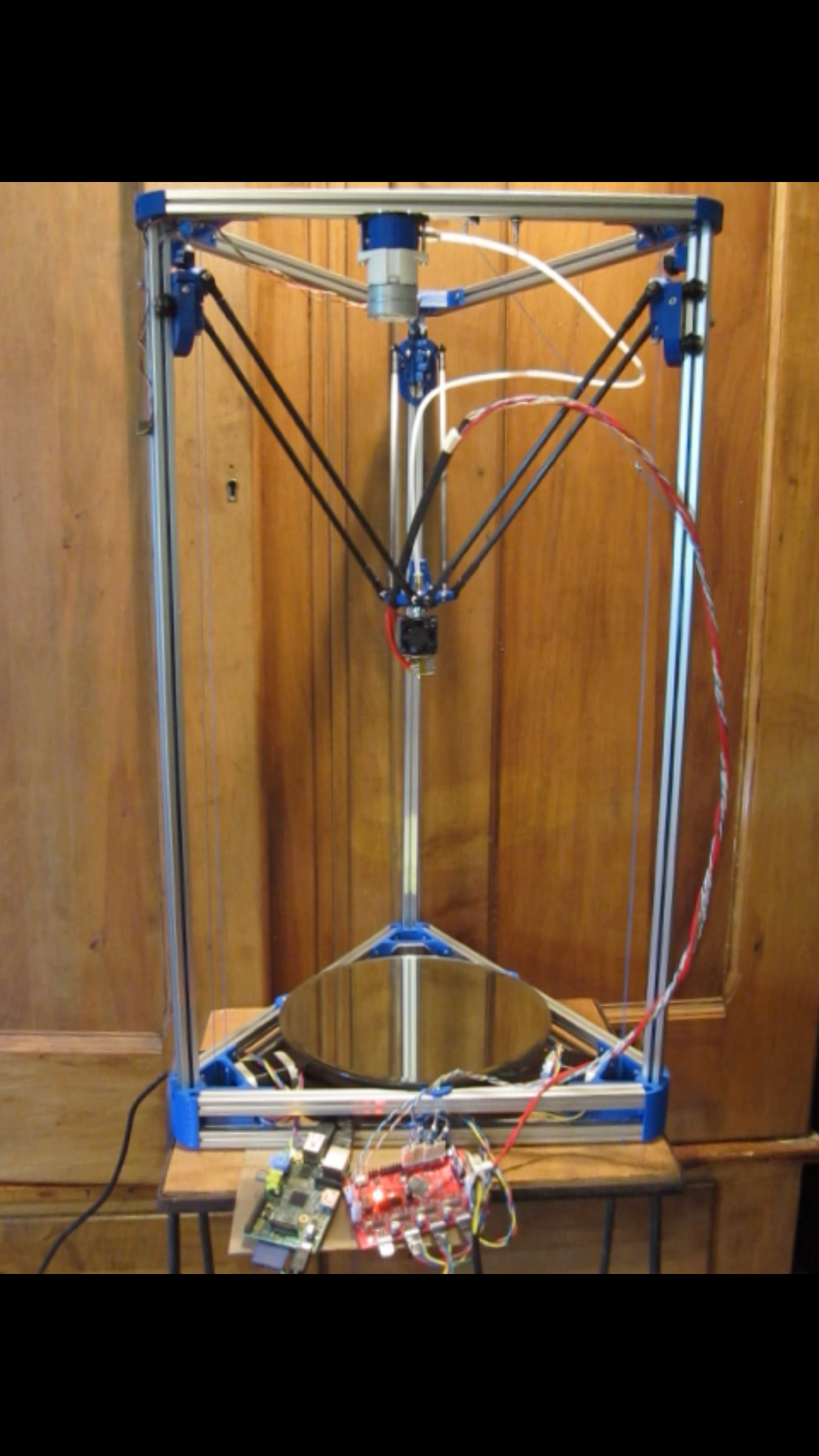
Kossel Deltabot 3D Printer
Early 3D printer
designs have a print-head or "hotend" that is moved by motors in
3 perpendicular directions, along the x, y, and z axes. A more
recent design places the hotend at the end of three arms that
are linked to tracks that allow movement in the vertical plane,
which translates into movement in the x, y, and z axes based on
the coordinated movement of the three arms. This is termed the
"Delta" geometry, and robots of this design are called
Deltabots. There are several advantages to this design and
perhaps a couple of disadvantages.
This Deltabot is a
variant of the Kossel Mini designed by Johann Rocholl, and
includes several customizations intended to reduce cost and
enhance it's versatility. The original Kossel Mini relies on an
aluminum rail and carriage system that is rather costly. The
very first deltabots used ball bearings that rode in the grooves
of the vertical columns, and while the metal on metal contact
was detrimental to the finish on the aluminum, delrin covers
have been developed to allow the bearings to ride in the grooves
without damage. These have been utilized here. The original
Kossel Mini was designed to use timing belts to transfer
movement from the motors to the carriages that ride on the
vertical columns. This build was altered to use 100 lb test
fishing line to reduce cost. This necessitated coming up with a
way to tension excess fishing line, so that the line could be
installed loosely and wound up to tighten it. A screw tensioning
system was devised, similar to a tensioner on a guitar, that
reels in the extra line, and final tension is adjusted as one
would with the stock Kossel, by the small screw at the top of
each column. V-wheel bearings replace timing belt idlers at the
tops of the columns. Many people opt for the J-head hotend on
their deltabots, but the E3D hotend was incorporated here
because of it's all-metal design which provides the potential to
use a wider variety of plastics that have higher melting
temperatures. Because of an ordering mishap during bill of
material changes the PG35l geared stepper motor was purchased
while the extruder components were designed to utilize a new
motor. This required some jerry-rigging to mesh the two
components and yield an operable extruder that would feed the
plastic filament off the reel to the hotend. The Kossel Mini was
equipped with a deployable probe that allowed for auto-leveling
and adapting the print code to the angle of the print surface.
Implementing this probe on this machine was problematic so a new
"direct probe" was designed to allow for direct probing of the
bed surface with the hotend. This probe is based on the design
of a touch probe digitizer used to "scan" 3d parts for CNC work.
An additional adaptation of the Kossel Mini allowed a dremel
flex tool to be mounted in place of the hotend, providing PCB
etching, drilling, and light milling capabilities.